Download the article in PDF format => vacuum electric furnaces for sintering products from powder materials
Sintering the metal and ceramic powder materials is one of the most important technological operations used in the powder metallurgy. The sintering method is used to manufacture components of machines, filters for purifying liquids and gases, sealing materials for gas turbines, as well as parts of vacuum and other equipment, contacts, ferrites for products of the electrical and radio engineering industry, etc. solid materials, permanent magnets, refractory metals and tantalum capacitors. Porous compact structures formed by sintering niobium hydride powder in vacuum as metal plates of niobium oxide-semiconductor capacitors are widely used in electronics. Of interest is the high-temperature sintering the plasma-chemical powders based on ZrO2, since such a ceramics have a high fracture toughness, and can be used as structural ones.
Vacuum sintering products made of magnetic and hard alloys, high-speed and tool steels, products based on nitrides and carbides is successfully carried out. The use of vacuum electric furnaces eliminates the main drawback of powder metallurgy technology. A large specific surface of the powders actively absorbs gases, which are then intensely released when the blanks are heated. This phenomenon is not eliminated even if sintering the blanks in electric furnaces with a protective atmosphere. During sintering in vacuum electric furnaces, gases from billets are removed much more easily and at lower heating temperatures. Vacuum not only protects powdered metals from interaction with chemically active components of the air atmosphere, but at the same time in some cases helps to reduce oxides content due to such a impurity as carbon contained in some powders. Heating within vacuum electric furnaces contributes to the evaporation of volatile impurities contained in many powdered metals.
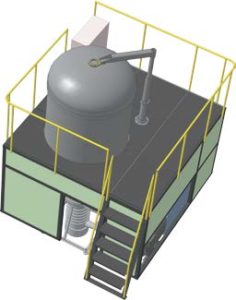
Also, for sintering blanks obtained by pressing can be used vacuum electric resistance furnaces of the brand “OTTOM”. Vacuum sintering furnaces are available in two different designs. The first version of vacuum electric furnaces is used for sintering without the application of plasticizers or after preliminary removal of plasticizers from the blanks. The second peculiariaty in some cases allows both operations (plasticizer removal and sintering) in one electric furnace. The preferred option is to pre-remove the plasticizer in a special electric furnace before carrying out in a stationary mode a one-stage sintering operation within a vacuum electric furnace. The figures show the last generation three versions of vacuum electric furnaces (2019 developments ) for sintering powder blanks. Figure 1 shows the model SNVE –2.4.2/16-OTTOM vacuum batch electric resistance furnace (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1. Vacuum batch electric furnace of resistance model SNVE-2.4.2/16-OTTOM.
Alphanumeric designation of model of the electric furnace of the SNVE-2.4.2/16-OTTOM model:
C — type of heating — resistance;
H – the main constructive feature – batch;
V – environment within the working space – vacuum;
E – thermoinsulation – all-metal;
2 – width of the working space, dm; (200 mm)
4 – depth of the working space, dm; (400 mm)
2 – height of the working space, dm; (200 mm)
16 – nominal temperature, hundreds ˚С.
OTTOM – is a registered trademark of the developer and manufacturer of electric furnaces.
The electric furnace allows the degassing of powder blanks and their sintering in vacuum at temperatures up to 1600 ° C. The work in the environment of high-purity neutral gases at excess pressure – no more than 0.02 MPa is allowed. Structurally, the electric furnace consists of the following parts: a vacuum chamber with a heating module, a vacuum system, a water cooling system, a furnace transformer, a power supply module with an automatic control system. Molybdenum heating module. Thermoinsulation – is the all metal. Additionally the heating module and thermal insulation based on carbon – carbon composite materials is available. The widespread use of this electric furnace is primarily purposed for preparation sintering powdersns of alloys in accordance with GOST 10160-75 (precision magnetic soft alloys, technical conditions), as well as for final sintering the hard alloys blanks.
Fig.2. Vacuum pit electric resistive furnace, model SShV-5.7/13-OTTOM
Alphanumeric — digital designation of the model of the electric furnace model SShV-5.7/13-OTTOM:
C – type of heating – resistance;
Sh – the main structural feature – pit;
V – environment within the working space – vacuum;
5 – diameter of the working space, dm; (500 mm)
7 – height of the working space, dm; (700 mm)
13 – nominal temperature, hundreds ˚С.
OTTOM – is a registered trademark of the developer and manufacturer of electric furnaces.
The vacuum pit electric resistive furnace model SShV-5.7/13-OTTOM is shown in Fig.2. It is purposed for the final sintering of powder blanks of various steels in the temperature range of 1150–1300 ° C. Structurally, the electric furnace consists of the following parts: the vertical vacuum chamber comprising the heating module on the frame of the service platform, an overpass, a mechanism for lifting and turning the lid, the pumping system, a water cooling system, a furnace transformer, an electrical power module with an automatic control system. Molybdenum heating module. Thermoinsulation – all metall. It can be equipped with a system of accelerated cooling and filling the vacuum chamber with an inert gas. Possible version of the heating module and therminsulation based on carbon – carbon composite materials. All elements of the furnace are mounted on a common frame, thus forming a single assembly and transport module.
Fig.3. Double-bell vacuum electric furnace model SGN-2.4-2/ 15-OTTOM
Alphanumeric designation of the model of the electric furnace model SGN-2.4-2 / 15-OTTOM:
C – type of heating – resistance;
G – the main constructive feature – bell;
H – is the environment within the working space (hydrogen);
2 – working space diameter, dm; (200 mm)
4 – height of the working space, dm; (400 mm)
2 – number of caps, pcs;
15 – nominal temperature, hundreds ˚С.
OTTOM is a registered trademark of the developer and manufacturer of electric furnaces.
The double-bell hydrogen – vacuum electric furnace бmodel СГН-2.4-2/ 15-OTTOMб is shown in fig. 3. The electric furnace is used not only for vacuum sintering, but also for heat treatment powder billet within the stream of dried hydrogen or withinin the atmosphere of high-purity inert gases. The electric furnace is a single constructive assembly and transport unit. The electric furnace is installed directly on the floor without a foundation. It has two heating chambers, alternately connected to a common power supply and control system. Each heating vacuum chamber consists of a fixed bottom part with a loading table and a hood lifted by an electromechanically driven mechanism. The heating module is made of molybdenum. Thermoinsulation – all metal. Before backfilling the chamber with hydrogen, pre-vacuuming is performed. Hydrogen exhaust is burned. The main purpose of the furnace – sintering the hard alloys. All represented electric furnaces are environmentally friendly. They do not emit active gases, which ensures high explosion and fire safety. In the case of use in the process of combustible gases (hydrogen), they use the afterburning system.